Industrial infrared heaters for thermal processes
Infrared heater transmit heat or energy contactless by means of electromagnetic waves. The infrared radiation is directed and does not require a transmission medium so that only the product is heated or thermally processed. Depending on the IR emitter temperature, bodies emit in the short, medium or long-wave infrared range. If the correct infrared radiator for the thermal process is selected, efficiency and throughput increase. IBT offers infrared radiant heaters for industrial manufacturing processes in all wavelength ranges, so that the optimum IR emitter is selected according to the requirements of your process.
Further information on infrared radiation or heat transfer can be found here.
Heater types and the optimization of the infrared radiation in your application
In order to use infrared in heat processes as efficiently as possible, it is necessary to select the right radiant heater. Thermal radiation or infrared radiation can be absorbed, transmitted and reflected by surfaces. The aim must be that the heated product absorbs as much radiation as possible. Depending on the wavelength of the IR radiation and the material of the product, the requirements for the radiant heater/infrared radiator differ.
Water, for example, absorbs particularly well in the medium-wave infrared range. Medium-wave infrared radiators are therefore particularly suitable for drying processes, such as the drying of water-based paints and other hydrous products. The same applies to plastics. However, also other criteria for emitter selection are the key. Reaction speed, required power density, lifetime and optional food suitability must be included in the decision making process.
Radiant heat or convection?
As a common drying process in the industrial sector convection solutions are mostly used. During convection drying, the air is heated. This in turn warms the body. This results in increased losses, both in heat transfer and in energy use. The heating of the medium is indirect and therefore very delayed. Furthermore, dust is whirled up by the circulating air. For example, in paint drying processes, this leads to unwanted impurities on the paint layer.
Infrared radiant heaters offer an optimal alternative. The heating of an intermediate medium is not required and thus takes place contactless. The direct heating and the missing intermediate medium minimizes heat losses. This is also accompanied by a lower energy input, which means radiant heat helps save energy. Due to the higher power density of the infrared radiators (up to 200 kW/m²), heating rates of up to 100 °C/s can be achieved.
In various applications, however, the process requires a combination of heat radiation and convection, for example during drying. The radiant heat causes the evaporation of the water on the surface of the material to be dried. It is released into the room air. Here the convection ensures the removal of moist air.
Electric heating elements: Infrared radiators and modules custom and mass produced
IBT GmbH offers a wide variety of infrared radiant heaters, which are particularly suitable for industry. Our product portfolio includes dimensions from spots over modules to complete system solutions. What is unique is that our product lines cover the entire wavelength spectrum of the short to long-wave infrared range regardless of the manufacturer.
In addition to the use of the established in the market infrared radiators in the industry, we develop custom-made heating elements for our customers, ranging from short runs to mass production. Most of our infrared heaters are electrically operated, but we also use gas-catalytic infrared heaters if required.
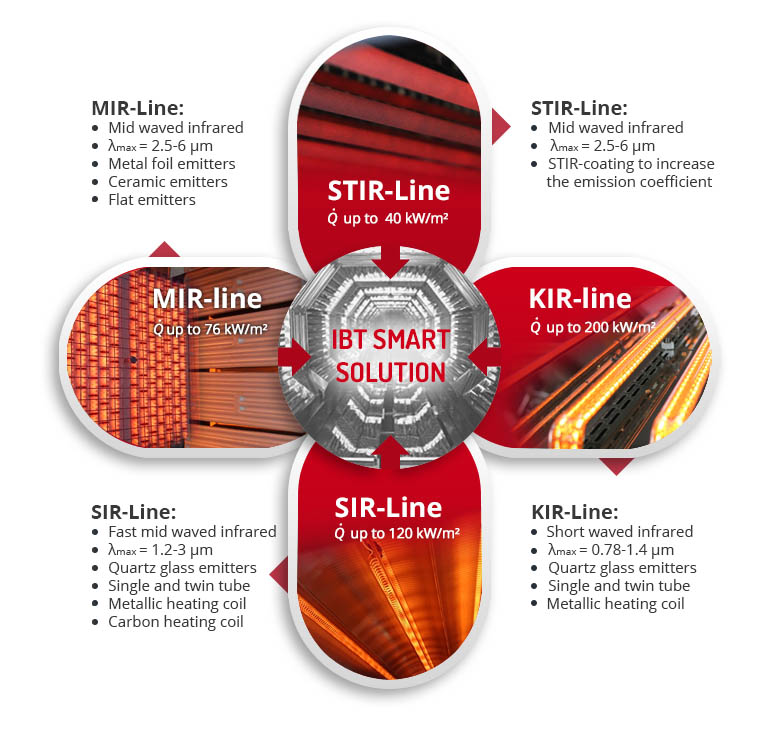
Overview industrial infrared heaters
KIR - short waved infrared:
- Metallic heating coil within a quartz glass tube filled with inert gas
- single tube/double tube emitter
- power density up to 200 kW/m² or 6.6 W/mm
- Very high reaction speed (1 s ON/OFF)
- Emitter temperature up to 2400 °C
- Wavelength of the emission maximum: 0.78 µm up to 1.4 µm
SIR – fast mid waved infrared:
- Heating coil within a quartz glass tube (evacuated or atmosphere) or metallic foil emitter
- Metallic or carbon heating coil
- power density up to 120 kW/m² or 3.3 W/mm
- High reaction speed (1-5 s ON/OFF)
- Emitter temperature up to 1400 °C
- Wavelength of the emission maximum: 1.4 µm up to 3.0 µm
STIR – mid waved infrared:
- Metallic heating coil within a quartz glass or ceramic tube
- STIR-coated quartz glass or ceramic tube to increase the emissivity
- Power density up to 40 kW/m² or 2 W/mm
- Low reaction speed (1-3 min ON/OFF)
- Emitter temperature up to 800 °C
- Wavelength of the emission maximum: 2.5 µm up to 6.0 µm
MIR – mid waved infrared:
- Metallic heating coil within a quartz glass tube or ceramic tube
- power density up to 76 kW/m²
- Low reaction speed (1-5 min ON/OFF)
- Emitter temperature up to 800 °C
- Wavelength of the emission maximum: 2.5 µm up to 6.0 µm
Ingolf Jaeger
Head of Sales
Dipl.-Ing. Mechanical Engineering
E-Mail: i.jaeger@ibt.de
Phone.: +49 (0) 3731 1683-15